If you have ever asked, “What is a VPN tunnel?” you are likely looking for a way to secure your digital life. Imagine sending a letter in a steel box instead of a clear envelope; that is essentially what a tunnel does for your data. At TurisVPN, we believe online privacy should be simple to understand.
In this guide, we break down exactly how this technology shields your personal information from prying eyes, hackers, and aggressive advertisers. We will cover everything from technical protocols to the differences between split and full tunneling. By the end, you will know exactly how to protect your digital footprint.
Alt: what is a vpn tunnel definition and encryption process
What Is a VPN Tunnel?
A VPN tunnel is an encrypted connection that links your device directly to the internet, shielding your data from outside observation.
To understand why this is necessary, we must examine how the internet typically functions. Normally, when you visit a website, your data travels openly. It moves from your device to your Internet Service Provider (ISP) and then to the site, meaning anyone watching can potentially see this traffic.
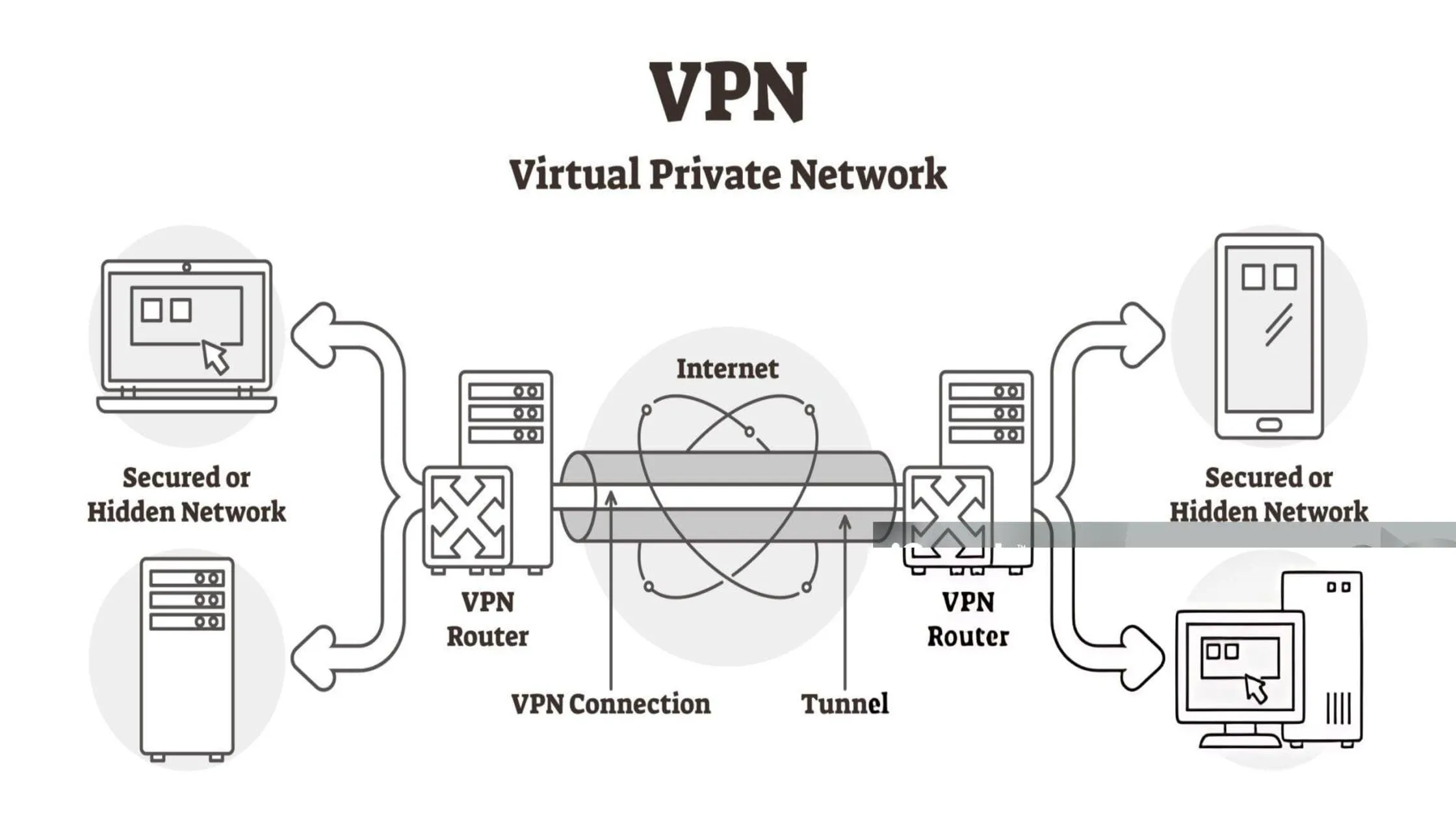
This private pathway completely changes that dynamic. Think of it like driving your car through a covered, underground tunnel instead of an open highway. Because the tunnel surrounds your data with encryption, it ensures that even if someone intercepts your traffic, they cannot read or understand it.
What Does a VPN Tunnel Do?

A VPN tunnel performs several critical tasks to keep your connection safe and private, effectively acting as a secure conduit for your data packets. Let’s explore the four main functions that answer the question, what is a VPN tunnel actually doing for you?
Encrypts data before it leaves your device
The moment you click a link, the tunnel scrambles your request, turning readable text into complex code through a process called encryption. Even if a hacker intercepts this data, it appears to them as gibberish. They cannot decode your passwords or messages, ensuring your information remains secure from the start.
Hides your IP address and online activities
Your IP address acts like your digital home address. It tells websites where you are. When you use a tunnel, websites see the VPN server’s IP, not yours. This masks your location effectively. It also prevents your ISP from logging your browsing habits. For more on this, read about how we ensure private browsing.
Protects your traffic on public Wi-Fi
Public Wi-Fi at cafes or airports is often unsafe. Hackers love these open networks. They can easily snoop on your connection. A VPN tunnel wraps your traffic in a protective layer. This blocks bad actors on the same network from seeing your data. It turns a risky public connection into a secure VPN without compromising your privacy.
Prevents ISP tracking and unauthorized interception
Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see everything you do. They can legally sell this data in many places. A VPN tunnel blinds them. They can see you are online, but they cannot see what you are doing. This stops them from throttling your speed based on your activity. It also addresses the concern of whether a VPN can hide your search history from your internet service provider.
How a VPN Tunnel Works (Step-by-Step)

Understanding what a VPN tunnel is requires examining the technical process, which occurs in the blink of an eye. This process ensures your data stays safe from point A to point B. Here is the step-by-step breakdown.
1. Handshake and key setup
First, your device establishes a connection to the VPN server. They perform a “handshake.” This verifies identity. They also agree on an encryption key. Only your device and the server know this key.
2. Creating the tunnel
Once the handshake is complete, the tunnel is formed. This is not a physical cable. It is a logical path across the internet. It is now ready to transport data securely.
3. Encapsulation and encryption
Your data gets placed inside a packet. Then, the VPN protocol wraps another packet around it. This is called encapsulation. The inner packet is encrypted. This is the essence of what a VPN tunnel is.
4. At the VPN server
The encrypted packet reaches the VPN server. The server uses the shared key to decrypt it. It removes the outer wrapper. Now, it can read the original request.
5. Return traffic back through the tunnel
The server sends your request to the website. The website responds to the server. The server encrypts this response and sends it back through the tunnel to you. Your device decrypts it.
VPN vs VPN Tunnel: What’s the Difference?
People often mix up these terms, but there is a slight distinction. A “VPN” (Virtual Private Network) refers to the entire service. It includes the servers, the app interface, the company, and features like a kill switch or ad blocker.
The “VPN Tunnel” is the specific mechanism the VPN uses to send data. It is the encrypted connection itself. You can think of the VPN as the car service, and the VPN tunnel as the protected route the car drives on. You cannot have a functional VPN without a tunnel. Understanding what a VPN tunnel is helps you appreciate the technology that powers the service.
Types of VPN Tunneling: Full vs. Split Tunneling

Not all tunnels work the same way; you can choose how your traffic flows. Sometimes you want total protection. Other times, you need speed for local apps. This brings us to the concepts of full and split tunneling.
What is Full Tunneling?
Full tunnel VPN is the standard setting. In this mode, all your internet traffic is routed through an encrypted tunnel. Every app, every browser tab, and every system update is secured. This offers maximum security. Nothing escapes the encryption.
If you want to ensure total privacy and utilize our no-logs policy, full tunneling is the best choice. It addresses the need for comprehensive coverage when considering what a VPN tunnel is capable of protecting.
What is Split Tunneling?
On the other hand, many users ask what a split-tunnel VPN is. This feature allows you to select which apps use the VPN and which do not. For example, you can route your web browser through the VPN for privacy. At the same time, your printer or banking app can use your direct internet connection. This is useful because some local services block VPNs.
So, what is split tunneling in a VPN good for? It optimizes speed. By not encrypting everything, you save bandwidth for tasks that need it. It gives you control. Finally, if you ever wondered what VPN split tunnelling is used for in gaming, it allows you to game on a local server while chatting on a secure app.
The Best VPN Tunneling Protocols Explained

The “rules” that determine how a tunnel is built are referred to as protocols. Different protocols offer different balances of speed and security. Choosing the right one is key to getting the best performance from TurisVPN.
OpenVPN
OpenVPN is the industry standard. It is open-source, meaning experts continually review it for vulnerabilities. It offers a great balance of speed and security. It is highly configurable. However, it can be heavy and slower on older devices.
WireGuard
WireGuard is the modern challenger. It uses newer code that is much lighter than OpenVPN. This makes it incredibly fast. It drains less battery on phones. It is quickly becoming the default for many users. It proves that a VPN tunnel can be both swift and secure.
IKEv2/IPsec
IKEv2/IPsec is excellent for mobile devices. It is very good at reconnecting if your Wi-Fi drops. For example, if you switch from Wi-Fi to data, IKEv2 maintains the VPN’s stability. It is fast and secure, though sometimes blocked by strict firewalls.
L2TP/IPsec
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol usually pairs with IPsec for encryption. It is easy to set up, but it can be slower. This is because it encapsulates data twice. It is decent, but newer protocols like WireGuard are usually better options today.
Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP)
PPTP is one of the oldest protocols. It is very fast because it has weak encryption. However, it is not secure by modern standards. Hackers can crack it easily. We generally do not recommend it unless you prioritise speed over privacy.
Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol (SSTP)
Owned by Microsoft, SSTP is a highly secure protocol. It can bypass most firewalls because it looks like normal web traffic (HTTPS). It works best on Windows, but is also available on other platforms. It is a solid choice for bypassing censorship.
Is a VPN Tunnel Safe?

Yes, a VPN tunnel is highly safe when using a reputable provider. However, safety depends on the encryption used (such as AES-256) and the protocol. A high-quality tunnel makes it nearly impossible for hackers to read your data. That said, you must trust the VPN provider not to log your data. At TurisVPN, we strictly adhere to a no-logs policy, ensuring that all data transmitted through a VPN tunnel remains private.
Common Risks When You Don’t Use a VPN Tunnel
Surfing the web without a tunnel leaves you vulnerable to various digital threats. Here is what can happen if you browse unprotected:
- Data Theft: Hackers on public Wi-Fi can steal your passwords and credit card numbers.
- ISP Tracking: Your internet service provider (ISP) tracks every site you visit and sells that information to advertisers.
- Bandwidth Throttling: ISPs may slow down your internet speed if they detect that you are streaming or gaming.
- Censorship: You may be unable to access content restricted in your region.
- Targeted Ads: Ad networks build a profile of you based on your IP address.
Understanding what a VPN tunnel is helps you avoid these pitfalls.
When a VPN Tunnel Is Not Enough (Limitations)
While a VPN is powerful, it is not a magic shield for everything. You should be aware of what it cannot do to manage your expectations.
VPN cannot hide you from websites you log into
If you log into Google or Facebook while using a VPN, they still know it is you. The tunnel hides your location, not your account identity. They will still track your activity on their platform.
VPN does not protect you from phishing
If you click a fake link in an email, a VPN cannot prevent you from doing so. It encrypts the traffic, but you are still sending data to a thief. You must still be vigilant against scams.
VPN does not make you anonymous like Tor
A VPN provides privacy, not total anonymity. For extreme anonymity, you might need Onion routing. Tor bounces traffic through many nodes, whereas a VPN uses one server (unless you use Multi-Hop).
VPN cannot fix malware already on your device
If your computer has a virus, a VPN cannot remove it. The virus can still steal data before it enters the tunnel. Always use antivirus software in conjunction with your VPN.
How TurisVPN Ensures a More Secure VPN Tunnel?
At TurisVPN, we go beyond the basics of what a VPN tunnel is to offer superior protection. We offer multi-hop connection features, which route your data through two servers for double encryption. This ensures that even if one server were compromised, your data remains safe.
We also support secure cryptocurrency transactions, protecting your anonymity while you manage your assets. Whether you are connecting multiple devices or just your phone, our infrastructure is built for speed and safety. We simplify what a VPN tunnel is so you can just click and connect. Whether you are connecting multiple devices or just your phone, our infrastructure is built for speed and safety. We simplify what a VPN tunnel is so you can just click and connect.
Bottom Line
If you were wondering what a VPN tunnel is, we hope this guide has clarified things for you. It is the essential technology that keeps your data safe from hackers, ISPs, and snoops. Encrypting your traffic and masking your IP gives you freedom and privacy.
Remember, you have options like split tunneling for convenience or full tunneling for total security. Protocols like WireGuard and OpenVPN ensure your connection is both fast and tough. While a VPN is not a cure-all, it is the first line of defense in cybersecurity. At TurisVPN, we are dedicated to making that defense as strong as possible. So, stop asking what a VPN tunnel is and start using one today to reclaim your digital rights.
FAQs
Q1. Do You Actually Need a VPN Tunnel?
Yes, if you value privacy. Without one, your data is vulnerable to your ISP and hackers, especially when using public Wi-Fi. It is essential for banking, streaming, and avoiding tracking. Knowing what is a vpn tunnel is the first step to protecting yourself.
Q2. Can my ISP see inside the VPN tunnel?
No, they cannot. They can see that you are connected to a VPN server and can track the amount of data being transferred. However, because of the encryption, they cannot see the content of websites you visit or messages you send.
Q3. Is SSH tunneling the same as a VPN tunnel?
They are similar but different. SSH tunneling is often used by tech experts to secure specific application traffic. A VPN tunnel secures all internet traffic from your device. For general users who are unfamiliar with what a VPN tunnel is, a VPN is the better, easier option for full protection.